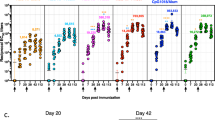
Squalene-based adjuvant compositions that can provide effective induction of specific humoral immune response have been developed. Recombinant receptor-binding domain (RBD) of surface S-protein of SARS-CoV-2 was used to evaluate the properties of the composition. Immunization of mice with the developed squalene-based compositions in combination with RBD allows obtaining high titers of specific antibodies: from 105 to 2×106. The blood sera from immunized mice exhibit neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (B.1.617.2) with a titer up to 1:2000.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Gregorio E, Caproni E, Ulmer JB. Vaccine adjuvants: mode of action. Front. Immunol. 2013;4:214. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00214.
Patent EA015817B1. Immunogenic composition comprising an oil in water emulsion adjuvant. Int. Cl. A61K 39/39, 30.12.2011.
Patent EA027142B1. Improved method for preparing squalene. Int. Cl. C07C 11/21, 30.06.2017.
Morel S, Didierlaurent A, Bourguignon P, Delhaye S, Baras B, Jacob V, Planty C, Elouahabi A, Harvengt P, Carlsen H, Kielland A, Chomez P, Garçon N, Van Mechelen M. Adjuvant System AS03 containing α-tocopherol modulates innate immune response and leads to improved adaptive immunity. Vaccine. 2011;29(13):2461-2473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.01.011
Seubert A, Monaci E, Pizza M, O’Hagan DT, Wack A. The adjuvants aluminum hydroxide and MF59 induce monocyte and granulocyte chemoattractants and enhance monocyte differentiation toward dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2008;180(8):5402-5412. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.8.5402
Cioncada R, Maddaluno M, Vo HTM, Woodruff M, Tavarini S, Sammicheli C, Tortoli M, Pezzicoli A, De Gregorio E, Carroll MC, D’Oro U, Piccioli D. Vaccine adjuvant MF59 promotes the intranodal differentiation of antigen-loaded and activated monocyte-derived dendritic cells. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0185843. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185843
Patent CN111388422A. Cationic squalene liposome and preparation method thereof (Translated). Int. Cl. A61K 47/18, 10.07.2020.
Patent EP-0745388-B2. Mammalian vaccines composition comprising squalene or squalane, phospholipid and a surfactant as adjuvant. Priority: 1995/06/02.
Facciolà A, Visalli G, Laganà A, Di Pietro A. An overview of vaccine adjuvants: current evidence and future perspectives. Vaccines (Basel). 2022;10(5):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050819
Zhang J, Hu Z, He J, Liao Y, Li Y, Pei R, Fang X, Zeng P, Fan R, Ou Z, Deng J, Zhou J, Guan W, Min Y, Deng F, Peng H, Zhang Z, Feng C, Xin B. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant interferon-armed RBD dimer vaccine (V-01) for COVID-19 in healthy adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase I trial. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021;10(1):1589-1597. https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2021.1951126
Starr TN, Czudnochowski N, Liu Z, Zatta F, Park YJ, Addetia A, Pinto D, Beltramello M, Hernandez P, Greaney AJ, Marzi R, Glass WG, Zhang I, Dingens AS, Bowen JE, Tortorici MA, Walls AC, Wojcechowskyj JA, De Marco A, Rosen LE, Zhou J, Montiel-Ruiz M, Kaiser H, Dillen JR, Tucker H, Bassi J, Silacci-Fregni C, Housley MP, di Iulio J, Lombardo G, Agostini M, Sprugasci N, Culap K, Jaconi S, Meury M, Dellota E Jr, Abdelnabi R, Foo SC, Cameroni E, Stumpf S, Croll TI, Nix JC, Havenar-Daughton C, Piccoli L, Benigni F, Neyts J, Telenti A, Lempp FA, Pizzuto MS, Chodera JD, Hebner CM, Virgin HW, Whelan SPJ, Veesler D, Corti D, Bloom JD, Snell G. SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies that maximize breadth and resistance to escape. Nature. 2021;597:97-102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03807-6
Coria LM, Saposnik LM, Pueblas Castro C, Castro EF, Bruno LA, Stone WB, Pérez PS, Darriba ML, Chemes LB, Alcain J, Mazzitelli I, Varese A, Salvatori M, Auguste AJ, Álvarez DE, Pasquevich KA, Cassataro J. A novel bacterial protease inhibitor adjuvant in RBD-based COVID-19 vaccine formulations containing alum increases neutralizing antibodies, specific germinal center b cells and confers protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. Front. Immunol. 2022;13:844837. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.844837
Kleanthous H, Silverman JM, Makar KW, Yoon IK, Jackson N, Vaughn DW. Scientific rationale for developing potent RBD-based vaccines targeting COVID-19. NPJ Vaccines. 2021;6(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-021-00393-6
Merkuleva IA, Shcherbakov DN, Borgoyakova MB, Shanshin DV, Rudometov AP, Karpenko LI, Belenkaya SV, Isaeva AA, Nesmeyanova VS, Kazachinskaia EI, Volosnikova EA, Esina TI, Zaykovskaya AV, Pyankov OV, Borisevich SS, Shelemba AA, Chikaev AN, Ilyichev AA. Comparative immunogenicity of the recombinant receptor-binding domain of protein S SARS-CoV-2 obtained in prokaryotic and mammalian expression systems. Vaccines (Basel). 2022;10(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10010096
Lodaya RN, Kanitkar AP, Ashraf A, Bamba D, Amiji MM, O’Hagan DT. A self-emulsified adjuvant system containing the immune potentiator alpha tocopherol induces higher neutralizing antibody responses than a squalene-only emulsion when evaluated with a recombinant Cytomegalovirus (CMV) pentamer antigen in mice. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(1):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 177, No. 2, pp. 188-192, February, 2024
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Volosnikova, E.A., Volkova, N.V., Ermolaev, V.V. et al. Use of Adjuvant Compositions Based on Squalene Ensures Induction of Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Bull Exp Biol Med 177, 221–224 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-024-06160-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-024-06160-6