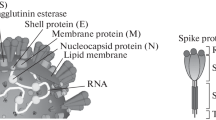
Abstract
The coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the urgent need for rapid, sensitive, and accurate diagnostic tests to detect SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19 disease. One promising approach is the use of aptamers, which are synthetic single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules possessing the ability to bind to specific targets with high affinity and specificity. In this study, we developed an aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor to detect the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, a viral antigen commonly utilized in diagnostic assays in a sandwich assay. To fabricate the electrochemical biosensor, a capture aptamer was immobilized onto a gold electrode. The target protein was introduced with a secondary aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticle (AuNP) to enhance the electrical signals. AuNPs were prepared by utilizing L-ascorbic acid or hyaluronic acid and were functionalized with a secondary aptamer. The secondary aptamer-conjugated AuNPs were first characterized to identify their physicochemical properties. The biosensor exhibited exceptional sensitivity and specificity, with a detection limit of 0.42 pg/mL, and showed no cross-reactivity with other respiratory viruses. The aptamer-based biosensor, coupled with secondary aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles, has significant potential as a rapid, cost-effective, and highly sensitive diagnostic tool for COVID-19, as well as for the detection of other infectious agents.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Data will be made available on request.
References
Gorbalenya, A.E., Baker, S.C., Baric, R.S., de Groot, R.J., Drosten, C., Gulyaeva, A.A., Haagmans, B.L., Lauber, C., Leontovich, A.M., Neuman, B.W., Penzar, D., Perlman, S., Poon, L.L.M., Samborskiy, D.V., Sidorov, I.A., Sola, I., Ziebuhr, J.: The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 5(4), 536–544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
Chan, J.F., Yuan, S., Kok, K.H., To, K.K., Chu, H., Yang, J., Xing, F., Liu, J., Yip, C.C., Poon, R.W., Tsoi, H.W., Lo, S.K., Chan, K.H., Poon, V.K., Chan, W.M., Ip, J.D., Cai, J.P., Cheng, V.C., Chen, H., Hui, C.K., Yuen, K.Y.: A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet 395(10223), 514–523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9
Tao, K., Tzou, P.L., Nouhin, J., Gupta, R.K., de Oliveira, T., Kosakovsky Pond, S.L., Fera, D., Shafer, R.W.: The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22(12), 757–773 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-021-00408-x
Jangra, S., Ye, C.J., Rathnasinghe, R., Stadlbauer, D., Krammer, F., Simon, V., Martinez-Sobrido, L., Garcia-Sastre, A., Schotsaert, M.: SARS-CoV-2 spike E484K mutation reduces antibody neutralisation. Lancet Microbe 2(7), E283–E284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00068-9
Plante, J.A., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Xia, H., Johnson, B.A., Lokugamage, K.G., Zhang, X., Muruato, A.E., Zou, J., Fontes-Garfias, C.R., Mirchandani, D., Scharton, D., Bilello, J.P., Ku, Z., An, Z., Kalveram, B., Freiberg, A.N., Menachery, V.D., Xie, X., Plante, K.S., Weaver, S.C., Shi, P.-Y.: Spike mutation D614G alters SARS-CoV-2 fitness. Nature 592(7852), 116–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2895-3
Vogels, C.B.F., Brito, A.F., Wyllie, A.L., Fauver, J.R., Ott, I.M., Kalinich, C.C., Petrone, M.E., Casanovas-Massana, A., Catherine Muenker, M., Moore, A.J., Klein, J., Lu, P., Lu-Culligan, A., Jiang, X., Kim, D.J., Kudo, E., Mao, T., Moriyama, M., Oh, J.E., Park, A., Silva, J., Song, E., Takahashi, T., Taura, M., Tokuyama, M., Venkataraman, A., Weizman, O.-E., Wong, P., Yang, Y., Cheemarla, N.R., White, E.B., Lapidus, S., Earnest, R., Geng, B., Vijayakumar, P., Odio, C., Fournier, J., Bermejo, S., Farhadian, S., Dela Cruz, C.S., Iwasaki, A., Ko, A.I., Landry, M.L., Foxman, E.F., Grubaugh, N.D.: Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT–qPCR primer–probe sets. Nat. Microbiol. 5(10), 1299–1305 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-020-0761-6
Liu, R., Han, H., Liu, F., Lv, Z., Wu, K., Liu, Y., Feng, Y., Zhu, C.: Positive rate of RT-PCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in 4880 cases from one hospital in Wuhan, China, from Jan to Feb 2020. Clin. Chim. Acta 505, 172–175 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.009
Wang, D., He, S., Wang, X., Yan, Y., Liu, J., Wu, S., Liu, S., Lei, Y., Chen, M., Li, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Hu, X., Zheng, X., Bai, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Song, M., Tang, Y.: Rapid lateral flow immunoassay for the fluorescence detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4(12), 1150–1158 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-020-00655-z
Bong, J.H., Lee, S.J., Jung, J., Sung, J.S., Kang, M.J., Lee, M., Jose, J., Pyun, J.C.: Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 using autodisplyaed Fv-antibodies on outer membrane of E. coli. BioChip J. 18(1), 146–159 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00139-1
Zeng, R., Qiu, M., Wan, Q., Huang, Z., Liu, X., Tang, D., Knopp, D.: Smartphone-based electrochemical immunoassay for point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Anal. Chem. 94(43), 15155–15161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03606
Egger, M., Bundschuh, C., Wiesinger, K., Gabriel, C., Clodi, M., Mueller, T., Dieplinger, B.: Comparison of the Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoassay with the EDI™ enzyme linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in human plasma. Clin. Chim. Acta 509, 18–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.05.049
Oh, D., Kim, J.S., Hwang, I.K., Park, H.S., Lee, C.S., Kim, T.H.: Real-time detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen using data analysis software and IoT-based portable reader with single-walled carbon nanotube field effect transistor. BioChip J. 17(3), 393–401 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-023-00116-0
Ha, Y., Kim, I.: Recent developments in innovative magnetic nanoparticles-based immunoassays: from improvement of conventional immunoassays to diagnosis of COVID-19. BioChip J. 16(4), 351–365 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00064-1
Bukkitgar, S.D., Shetti, N.P., Aminabhavi, T.M.: Electrochemical investigations for COVID-19 detection-A comparison with other viral detection methods. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 127575 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127575
Lou, B., Liu, Y., Shi, M., Chen, J., Li, K., Tan, Y., Chen, L., Wu, Y., Wang, T., Liu, X., Jiang, T., Peng, D., Liu, Z.: Aptamer-based biosensors for virus protein detection. Trends Analyt. Chem. 157, 116738 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116738
Wang, L., Wang, X., Wu, Y., Guo, M., Gu, C., Dai, C., Kong, D., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Qu, D., Fan, C., Xie, Y., Zhu, Z., Liu, Y., Wei, D.: Rapid and ultrasensitive electromechanical detection of ions, biomolecules and SARS-CoV-2 RNA in unamplified samples. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6(3), 276–285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00833-7
Zhang, Z., Sen, P., Adhikari, B.R., Li, Y., Soleymani, L.: Development of nucleic-acid-based electrochemical biosensors for clinical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 61(50), e202212496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202212496
Tieu, M.V., Pham, D.T., Le, H.T.N., Hoang, T.X., Cho, S.B.: Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of staphylococcus aureus using a gold-interdigitated single-wave-shaped electrode (Au-ISWE) electrochemical biosensor. BioChip J. 17(4), 507–516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-023-00126-y
Mandal, M., Dutta, N., Dutta, G.: Aptamer-based biosensors and their implications in COVID-19 diagnosis. Anal. Methods 13(45), 5400–5417 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ay01519b
Svobodova, M., Skouridou, V., Jauset-Rubio, M., Vieitez, I., Fernandez-Villar, A., Cabrera Alvargonzalez, J.J., Poveda, E., Bofill, C.B., Sans, T., Bashammakh, A., Alyoubi, A.O., O’Sullivan, C.K.: Aptamer sandwich assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antigen. ACS Omega 6(51), 35657–35666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c05521
Kumar, N., Shetti, N.P., Jagannath, S., Aminabhavi, T.M.: Electrochemical sensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132966 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132966
Song, S., Wang, L., Li, J., Fan, C., Zhao, J.: Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem. 27(2), 108–117 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.004
Zhang, Y., Juhas, M., Kwok, C.K.: Aptamers targeting SARS-CoV-2: a promising tool to fight against COVID-19. Trends Biotechnol. 41(4), 528–544 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.07.012
Abrego-Martinez, J.C., Jafari, M., Chergui, S., Pavel, C., Che, D., Siaj, M.: Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: nanoscale electrode-aptamer-SARS-CoV-2 imaging by photo-induced force microscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 195, 113595 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113595
Kang, H., Buchman, J.T., Rodriguez, R.S., Ring, H.L., He, J., Bantz, K.C., Haynes, C.L.: Stabilization of silver and gold nanoparticles: preservation and improvement of plasmonic functionalities. Chem. Rev. 119, 664–699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00341
Alexandridis, P.: Gold nanoparticle synthesis, morphology control, and stabilization facilitated by functional polymers. Chem. Eng. Technol. 34(1), 15–28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201000335
Kim, E.J., Yeum, J.H., Choi, J.H.: Effects of polymeric stabilizers on the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 107–111 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.11.012
Daruich De Souza, C., Ribeiro Nogueira, B., Rostelato, M.E.C.M.: Review of the methodologies used in the synthesis gold nanoparticles by chemical reduction. J. Alloy. Compd. 798, 714–740 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.153
Boca, S.C., Potara, M., Toderas, F., Stephan, O., Baldeck, P.L., Astilean, S.: Uptake and biological effects of chitosan-capped gold nanoparticles on Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 31(2), 184–189 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.08.015
Kim, H.M., Park, J.H., Choi, Y.J., Oh, J.M., Park, J.: Hyaluronic acid-coated gold nanoparticles as a controlled drug delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs. RSC Adv. 13(8), 5529–5537 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra07276a
Annur, S., Santosa, S.J., Hidayat, A.N.: pH dependence of size control in gold nanoparticles synthesized at room temperature. Orient. J. Chem. 34(5), 2305–2312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/340510
Shrivastava, A.: Introduction to plastics engineering. William Andrew, Cambridge, MA (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2014-0-03688-X
Tian, J., Liang, Z., Hu, O., He, Q., Sun, D., Chen, Z.: An electrochemical dual-aptamer biosensor based on metal-organic frameworks MIL-53 decorated with Au@Pt nanoparticles and enzymes for detection of COVID-19 nucleocapsid protein. Electrochim. Acta 387, 138553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138553
Fabiani, L., Saroglia, M., Galatà, G., De Santis, R., Fillo, S., Luca, V., Faggioni, G., D’Amore, N., Regalbuto, E., Salvatori, P., Terova, G., Moscone, D., Lista, F., Arduini, F.: Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: a reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 171, 112686 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112686
Yakoh, A., Pimpitak, U., Rengpipat, S., Hirankarn, N., Chailapakul, O., Chaiyo, S.: Paper-based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 176, 112912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112912
Amouzadeh Tabrizi, M., Acedo, P.: An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based aptasensor for the determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD using a carbon nanofiber-gold nanocomposite modified screen-printed electrode. Biosensors-Basel 12(3), 142 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030142
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology as ‘Development of fiber-based technology for reduction of hazardous substances in the air (KITECH EO-23-0005)’ and by the Gachon University research fund of 2023(GCU-202401120001).
Funding
Korea Institute of Industrial Technology, KITECH EO-23-0005, Junghun Park,Gachon University, GCU-202401120001, Junghun Park.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hyoung-Mi Kim: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft. Junghun Park: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that may have influenced the work reported in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HM., Park, J. Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Using an Aptamer Sandwich Assay-Based Electrochemical Biosensor. BioChip J 18, 622–632 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00174-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00174-y