Abstract
Background
Solid organ transplant recipients taking immunosuppressive drugs are at greater risk of severe COVID-19 than the general population. In particular, kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) are known to have lower seropositivity after basal doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, and the strategy of administering booster doses in these immunocompromised individuals has been promoted worldwide.
Methods
This study evaluated the effect of a fourth dose (D4) of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Japanese KTRs. Anti-spike (anti-S) IgG antibody titers at 1 and 3 months after D4 of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine were evaluated in 75 KTRs.
Results
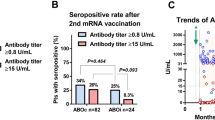
The median anti-S IgG antibody titers at 1 and 3 months after D4 were 4728.1 (interquartile range [IQR]: 643.2–13,953.1) AU/mL and 3778 (IQR: 642–9436.6) AU/mL, respectively. The seropositivity rate after D4 was 85.1% at 1 month and 83.1% at 3 months, and the seroconversion rate was 28.6% (4 of 14 KTRs seronegative after the third dose). Factors associated with poor humoral responses were shorter time post-transplant to infection, a higher mycophenolate mofetil dose, a lower lymphocyte count, and a lower estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates some efficacy of D4 of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in KTRs who are seronegative after three doses and encourages consideration of further booster doses of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.




Similar content being viewed by others

Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–42.
Frenck RW Jr, et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(3):239–50.
Tregoning JS, et al. Progress of the COVID-19 vaccine effort: viruses, vaccines and variants versus efficacy, effectiveness and escape. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(10):626–36.
Banerjee D, et al. COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2020;97(6):1076–82.
Kremer D, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: Lessons to be learned. Am J Transpl. 2021;21(12):3936–45.
Phadke VK, Scanlon N, Jordan SC, Rouphael NG. Immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in solid organ transplant recipients. Curr Transpl Rep. 2021;8(2):127–39.
Benotmane I, et al. Antibody response after a third dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients with minimal serologic response to 2 doses. JAMA. 2021;326(11):1063–5.
Kamar N, et al. Three doses of an mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(7):661–2.
Hall VG, et al. Randomized trial of a third dose of mRNA-1273 vaccine in transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(13):1244–6.
Kuniduzi Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fourth dose of the COVID-19 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transpl Immunol. 2023;79:101864.
Kawabe M, et al. Booster effect of the third dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in Japanese kidney transplant recipients. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9976.
Ohki Y, et al. Long-term humoral response after a second dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in Japanese kidney transplant recipients. Front Microbiol. 2022;9(13):922042.
Benotmane I, et al. A fourth dose of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine improves serum neutralization against the Delta variant in kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2022;101(5):1073–6.
Brandstetter C, et al. Humoral response after a third and fourth dose of mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in previously seronegative kidney transplant recipients. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2022;134(23–24):815–21.
Cristelli MP, et al. The fourth dose of CoronaVac vaccine results in a small increase of seroconversion and antibody values among kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2022;106(9):e420–1.
Benotmane I, et al. Low immunization rates among kidney transplant recipients who received 2 doses of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021;99(6):1498–500.
Dębska-Ślizień A, et al. Predictors of humoral response to mRNA COVID19 vaccines in kidney transplant recipients: a longitudinal study—the COViNEPH project. Vaccines (Basel). 2021;9(10):1165.
Frölke SC, et al. Predictors of nonseroconversion to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in kidney transplant recipients. Transpl Direct. 2022;8(11): e1397. https://doi.org/10.1097/TXD.0000000000001397.
Masset C, et al. A fourth SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in strictly seronegative kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2022;101(4):825–6.
Rozen-Zvi B, et al. Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine among kidney transplant recipients: a prospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021;27(8):1173.e1-1173.e4.
Midtvedt K, et al. Fourth dose of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients with previously impaired humoral antibody response. Am J Transpl. 2022;22(11):2704–6.
Toapanta N, et al. Kidney transplantation and COVID-19 renal and patient prognosis. Clin Kidney J. 2021;14(Suppl 1):i21–9.
Japanese Society for Transplantation COVID-19 Task Force. Available online at: https://square.umin.ac.jp/jst-covid-19/images/20220831covid-19cases.pdf. Accessed on 23 Nov 2022.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Available online at: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10906000/000970173.pdf. Accessed on 23 Nov 2022.
Sahota A, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of COVID-19 infection in a large cohort of solid organ transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2022;106(12):2426–34.
Rahimzadeh H, et al. The tsunami of COVID-19 infection among kidney transplant recipients: a single-center study from Iran. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021;11(4):389–96.
Elias M, et al. COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients: disease incidence and clinical outcomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31(10):2413–23.
Feng S, et al. Correlates of protection against symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. 2021;27(11):2032–40.
Gilbert PB, et al. Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science. 2022;375(6576):43–50.
Moss P. The T cell immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat Immunol. 2022;23(2):186–93.
Sekine T, et al. Robust T cell immunity in convalescent individuals with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell. 2020;183(1):158-168.e14.
Vardhana S, et al. Understanding T cell responses to COVID-19 is essential for informing public health strategies. Sci Immunol. 2022;7(71):eabo1303.
Acknowledgements
This research received no specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors. We thank Teruko Tamatsukuri, University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan, for her expert assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.H., M.K., I.Y., and Hiroyasu Yamamoto participated in the clinical practice, designed the study protocol, and drafted the manuscript. Y.O., A.K., N.M., Y.T., T.H., and I.O. participated in patient care and revised the manuscript. F.U., J.M., Hiroki Yamada, and T.K. performed kidney transplantation. T.Y. supervised all authors as division director. All authors participated in the preparation of the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee at which the studies were conducted (IRB approval number 33-314 [10934]) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, A., Kawabe, M., Yamamoto, I. et al. Booster effect of the fourth dose of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in kidney transplant recipients. Clin Exp Nephrol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-025-02651-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-025-02651-6